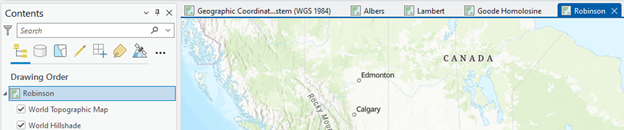
4. Create multiple data frames
The primary objective of this lab is to investigate how coordinate systems and map projections represent shapes and areas differently. In doing so, we will 2) generate three more Maps, 2) copy the USA_48 to each Map, and 3) apply three different map projections, in this case, Albers Equal Area Conic, Lambert Conformal Conic, and Robins, to the USA_48 layer in each Map.
1. Name the current Map to “Geographic.” Right-click on the Map in the Contents pane, choose Properties, and click General. Type Geographic Coordinate System (WGS 1984) in the Name blank and click OK.
2. Now, you will add a new Map in the ArcGIS Pro. In the Insert tab in the ribbon, click the New Map button. A new Map pops up:
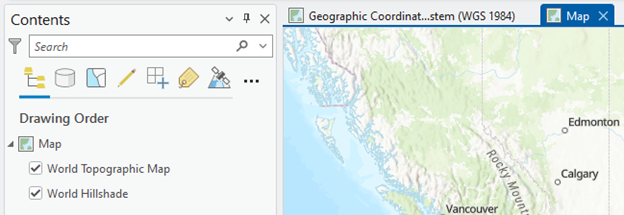
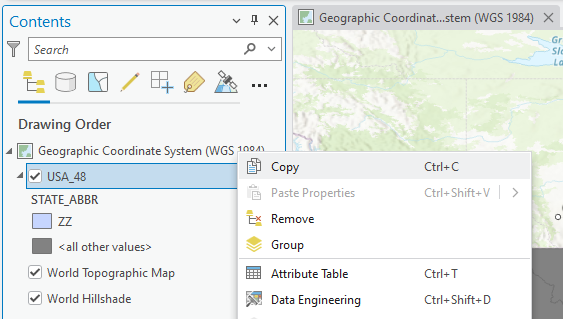
3. We will copy the USA_48 layer from the Geographic Coordinate System (WGS 1984) Map to the new Map. Click the Geographic tab, right-click on USA_48, and click Copy:
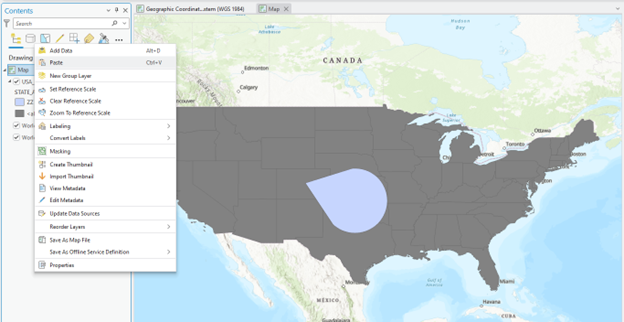
4. Click Map (right next to the Geographic), right-click Map in the Contents pane, and choose Paste. Now USA_48 is added to the new Map:
5. We will transform the USA_48 layer in the new Map into the “Albers Equal Area Conic” projection. In Geoprocessing, type Project and open it. Fill in the Parameters like:
-
- Input Dataset or Feature Class: USA_48
- Output Dataset or Feature Class: USA_48_Albers
- Output Coordinate System: Click the Globe icon and expand Projected Coordinate System > Continental > North America > North America Albers Equal Area Conic
Stop and Further Study: The Geographid Transformation blank says “GWS_1985(ITRF00)_To_NAD_1983. Two takeaways from this Default message are,
- The Project tool automatically detects the Geographic Coordinate Systems disparity between the original layer (i.e., USA_48) and the map projection that we want to apply (i.e., North America Albers Equal Area Conic). In other words, the Alber Equal Area Conic map projection system has “NAD 1983” as its Geographic Coordinate System (GCS). As the original “USA_48” layer has “WGS 1984” as its GCS, the map project tool decides to transform the GCS from WGS 1984 to NAD 1983.
- Have you noticed “underscores” in the spaces between words, such as “_To_NAD_?” Note that digital information systems may result in unexpected errors if they encounter blank spaces, so please fill in the space with “underscores” when you use ArcGIS software.
6. Click Run
7. We will change the Map frame’s coordinate system to match the USA_48_Albers. Right-click Map and choose Properties:
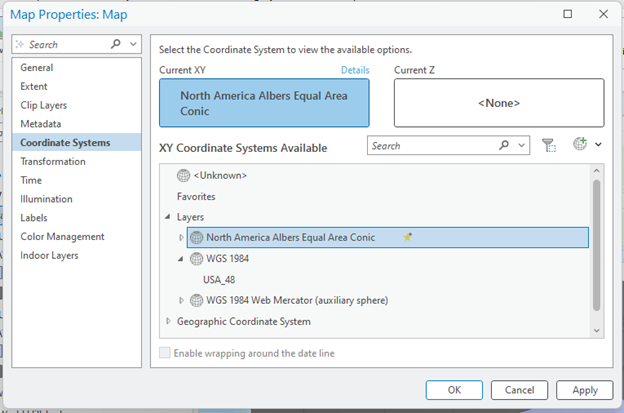
7. Click Coordinate Systems, choose North America Albers Equal Area Conic as the Map frame’s coordinate systems, and click OK:
Stop and Observe: Did you notice something different from the previous view?
8. Remove the USA_48 layer in the current Map frame.
9. Let’s change the map frame name and coordinate system. Right-click on Map in the Contents pane, choose Properties, and click General. Type Albers in the Name blank and click OK.
10. Next, you will transform USA_48 into the “Lambert Conformal Conic” projection. Repeat 1) inserting another Map frame, 2) copying the USA_48 layer from the Geographic Map and pasting it to the new Map frame, and 3) changing the projection with the Project tool, like:
-
- Input Dataset or Feature Class: USA_48
- Output Dataset or Feature Class: USA_48_Lambert
- Output Coordinate System: Click the drop-down icon and expand Projected Coordinate System > Continental > North America > North America Lambert Conformal Conic.
11. The last two map projections you will apply are the world map projections, such as Goode Homolosine and Robinson. Repeat the changing projection process like:
-
- Input Dataset or Feature Class: USA_48
- Output Dataset or Feature Class: USA_48_Robinson
- Output Coordinate System: Click the drop-down icon and expand Projected Coordinate System > Projected Coordinate System > World > Goode Homolosine (or Robinson (world)).
Now, we have FIVE Map frames in the ArcGIS Pro: