4 Adaptive Restraints
On This Page
- Additional Information about Adaptive Restraints
- Types of Specialized Restraints
- Car Seat Use After a Crash
- School Bus Restraints
Adaptive Restraints – Designed for Children Who:
- Are unable to use conventional harness system
- Have outgrown conventional car seat and require additional postural support
- Must lie down
- Demonstrate severe behavioral challenges, escaping/eloping
Additional Information about Adaptive Restraints
- Not readily available
- More expensive than conventional seats
- Utilize insurance for coverage
- Orders must go through local durable medical equipment (DME) providers
- Can take months to acquire

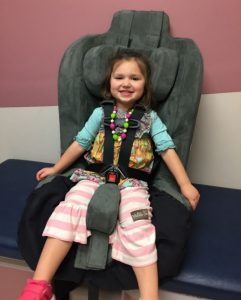
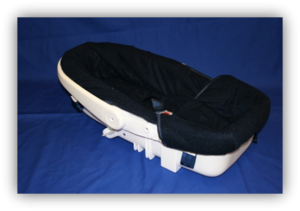
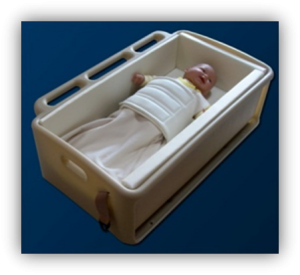
Types of Specialized Restraints
- Car Beds
- Jefferson Car Seat
- Adaptive Restraints for Casts
- Large Medical Seats
- Adaptive Booster Seats
- Adaptive Vests
Car Beds
- For infants and younger children who must lie down
- Prone or right-side positioning requires physician’s order
- All car beds installed lengthwise on vehicle bench seat with child’s head toward center of vehicle

Jefferson Car Seat
- Rear-Facing Only
- Designed for children 7.5-40 pounds, 19-37 inches
- Special yoke harness design for omphaloceles
- Padding and positioning prevents buckle/harness contact with omphalocele/abdomen

Adaptive Restraints for Casts
- Convertible car seat designed for arm and leg casts
- Rear-facing 5-40 pounds
- Forward-facing 22-80 pounds
- Hope Car Bed (if need to lie down)
- Lay Down EZ-ON Vest (if need to lie down)
- Spirit Spica (forward-facing only)

- Hope Car Bed (if need to lie down)
- Lay Down EZ-ON Vest (if need to lie down)
- Spirit Spica (forward-facing only)



Large Medical Seats
- Forward-facing only
- Lower weight 20-35 pounds
- Upper weight 102-130 pounds
- 5-point harness restraint

- Standard and Optional Accessories to Improve Positioning:
- Abductors
- Seat extenders
- Lateral supports
- Head supports
- Anti-escape options on some large medical seats

Adaptive Booster Seats
- Forward-facing only
- Lower weight 20-79 pounds
- Upper weight 108-175 pounds
- Require lap-and-shoulder belt over child for crash protection
- 5-point harness or vest for postural support
- Wedges and abductors for hip and pelvis positioning

Adaptive Vests
- Forward-facing only
- Lower weight 31-81 pounds
- Upper weight 168-225 pounds
- Require lap-and-shoulder belt over child for crash protection
- Vests for postural support
- Leg straps for hip and pelvis positioning

Car Seat Use After a Crash
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) recommends that car seats be replaced following a moderate or severe crash in order to ensure a continued high level of crash protection for child passengers. Car seats do not automatically need to be replaced following a minor crash.
- Refer to your specific car seat manual for information

What defines a minor crash?
- A minor crash is one in which ALL of the following apply:
- The vehicle was able to be driven away from the crash site.
- The vehicle door nearest the car seat was not damaged.
- None of the passengers in the vehicle sustained any injuries in the crash.
- If the vehicle has air bags, the air bags did not deploy during the crash; and
- There is no visible damage to the car seat.
- NEVER use a car seat that has been involved in a moderate to severe crash.
- Always follow manufacturer’s instructions.
School Bus Restraints
- Restraint options:
- Integrated bus seats
- Conventional restraints
- Adaptive restraints
- School bus specific restraints
- Availability of seat belts on bus affects restraint selection
- Some restraints attach to school bus seat without seat belt


