10.4 Promotional Mix: Personal Selling and Sales Management
Introduction
Personal selling is when a company uses salespersons to build a relationship and engage customers to determine their needs and attain a sales order that may not otherwise have been placed. The personal selling process is a seven step approach: prospecting, pre-approach, approach, presentation, meeting objections, closing the sale, and follow-up. In addition to the sales effort, sales management has become an integral part of any organization’s marketing strategy. The sales manager is the bridge between the company and its salespeople, ensuring that objectives and policies are being met. To understand the importance of the sales, keep in mind that what the salespeople accomplish create the top line – or revenue – for an organization. Without them, there would be not be a positive bottom line.
Types of Salespeople
There are different ways to categorize salespeople. They can be categorized by the customers they work with, such as whether they are consumers, other businesses, or government institutions. Another way to categorize salespeople is by the size of their customers. Most professional sales positions involve selling to other businesses, but many also sell to consumers like you. There are three general types of salespeople: order getters, order takers, and sales support.
Order getters are responsible for generating new sales by prospecting and acquiring new customers. Depending on the industry, this can be a very time consuming process as multiple bids and meetings are conducted to try and ‘win’ a potential customer’s business.
Order takers primarily deal with existing customers. Often the term Account Manager is used for order takers. They are responsible for being the ‘face’ of the company to the customer and to work with the customer to ensure their needs are being met and expectations are exceeded.
Support personnel are professionals not directly involved in the sales or revenue generating process, but nonetheless have an important role to play in a company’s success. While support personnel are often seen as those providing after-sales service or technical assistance, the definition of support staff also includes functions such as accounting, finance, human resources, supply chain, etc. Other common support roles that work with sales managers directly or assist clients and customers with product and service issues include sales engineers, technical support specialists, and customer support representatives.
In some organizations, these are three very distinct roles. In other organizations, one person may assume all three roles at different times. There is not a right or wrong way to organize the sales force in this manner but care needs to be given that the customers’ best interest is always the main consideration.
The Sales Process
The typical sales process involves several stages, beginning with the preapproach and ending with customer service. In between are other stages, such as the needs-identification stage, presentation stage, and closing stage (see Figure 10.4.1 “The Typical Sales Process”).
The preapproach is the planning stage. During this stage, a salesperson may use LinkedIn to find the right person to call and to learn about that person. In addition, a Google search may be performed to find the latest news on the company, while a search of financial databases, such as Standard & Poor’s, can provide additional news and information. A salesperson may also search internal data in order to determine if the potential buyer has any history with the company. Note that such extensive precall planning doesn’t always happen; sometimes a salesperson is literally just driving by, sees a potential customer, and decides to stop in, but in today’s information age, a lot of precall planning can be accomplished through judicious use of Web-based resources.
In the approach, the salesperson attempts to capture enough of the prospective customer’s attention and interest in order to continue the sales call. If it is a first-time call, introductions are needed. A benefit that could apply to just about any customer may also be offered to show that the time will be worthwhile. In this stage, the salesperson is attempting to convince the buyer to spend time exploring the possibility of a purchase.
Figure 10.4.1: The Typical Sales Process – this graphic shows the steps in the sales process that are described within in the text
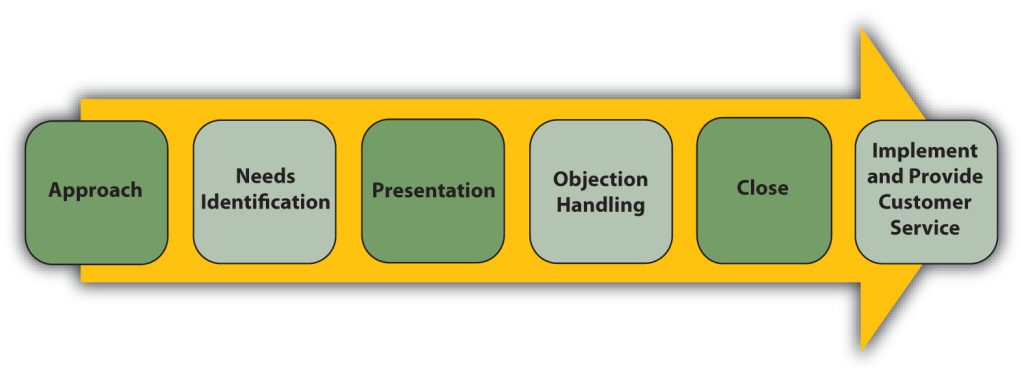
A typical sales process starts with the preapproach and move through several stages to the close. Good salespeople continue with making sure the customer gets the product, uses it right, and is happy with it.
With the buyer’s permission, the salesperson then moves into a needs identification section. In complex situations, many questions are asked, perhaps over several sales calls. These questions will follow the SPIN outline or something similar. Highly complex situations may require that questions be asked of many people in the buying organization. In simpler situations, needs may not vary across customers so a canned presentation is more likely. Then, instead of identifying needs, needs are simply listed as solutions are described.
A presentation is then made that shows how the offering satisfies the needs identified earlier. One approach to presenting solutions uses statements called FEBAs. FEBA stands for feature, evidence, benefit, and agreement. The salesperson says something like, “This camera has an automatic zoom [Feature]. If you look at the viewfinder as I move the camera, you can see how the camera zooms in and out on the objects it sees [Evidence]. This zoom will help you capture those key moments in Junior’s basketball games that you were telling me you wanted to photograph [Benefit]. Won’t that add a lot to your scrapbooks [Agreement]?”
Note that the benefit was tied to something the customer said was important. A benefit only exists when something is satisfying a need. The automatic zoom would provide no benefit if the customer didn’t want to take pictures of objects both near and far.
Objections are concerns or reasons not to continue that are raised by the buyer, and can occur at any time. A prospect may object in the approach, saying there isn’t enough time available for a sales call or nothing is needed right now. Or, during the presentation, a buyer may not like a particular feature. For example, the buyer might find that the automatic zoom leads the camera to focus on the wrong object. Salespeople should probe to find out if the objection represents a misunderstanding or a hidden need. Further explanation may resolve the buyer’s concern or there may need to be a trade-off; yes, a better zoom is available but it may be out of the buyer’s price range, for example.
When all the objections are resolved to the buyer’s satisfaction, the salesperson should ask for the sale. Asking for the sale is called the close, or a request for a decision or commitment from the buyer. In complex selling situations that require many sales calls, the close may be a request for the next meeting or some other action. When the close involves an actual sale, the next step is to deliver the goods and make sure the customer is happy.
There are different types of closes. Some of these include:
- Direct request: “Would you like to order now?”
- Minor point: “Would you prefer red or blue?” or “Would you like to view a demonstration on Monday or Tuesday?”
- Summary: “You said you liked the color and the style. Is there anything else you’d like to consider before we complete the paperwork?”
When done properly, closing is a natural part of the process and a natural part of the conversation. But if pushed inappropriately, buyers can feel manipulated or trapped and may not buy even if the decision would be a good one.
The sales process used to sell products is generally the same regardless of the selling strategy used. However, the stage being emphasized will affect the strategy selected in the first place. For example, if the problem is a new one that requires a customized solution, the salesperson and buyer are likely to spend more time in the needs identification stage. Consequently, a needs-satisfaction strategy or consultation strategy is likely to be used. Conversely, if it’s already clear what the client’s needs are, the presentation stage is likely to be more important. In this case, the salesperson might use a script-based selling strategy, which focuses on presenting a product’s benefits rather than questioning the customer.
Sales Management
Introduction
Sales operations are a set of business activities and processes that help a sales organization run effectively, efficiently, and in support of business strategies and objectives. Sales operations may also be referred to as sales operations, sales support, or business operations. The set of sales operations activities vary from company to company but often include these categories:
- Sales strategy: design, planning, execution;
- Measurement of results: reporting, analytics and sales data;
- Compensation, sales quota, policies;
- Technology and tools, including CRM;
- Training and sales communication;
- Sales territory design and optimization;
- Contests/spiffs;
- Lead generation/sales programs; and
- Customer segmentation.
We will not discuss all of these categories but will highlight the major responsibilities of sales managers.
Creating The Sales Force Structure
How will the sales process be structured? The answer to that question, an important one, depends on the company’s strategy. The resulting structure will guide the sales force and their actions and will, therefore, impact the company’s bottom line.
When developing the sales force structure, sales managers must:
- Figure out the right mix of generalists, product, market, or activity specialist with the objective of balancing sales force productivity. What is the right mix? That depends on the company and it’s offerings.
- Design a reporting structure that makes it easy to both coordinate and control the sales process and the activities of the salespeople.
- Help the sales people achieve their goals (and reduce stress) by providing training, coaching, incentives, information support, and performance management.
Effective Job Design
Job design, defined as the allocation of specific work tasks to individuals and groups, is critical for any organization. Allocating jobs and tasks means specifying the contents, methods, and relationships of jobs to satisfy technological and organizational requirements as well as the personal needs of jobholders. If successful job design is not implemented, then the company’s general strategy and direction will be strongly diverted. Employees, in turn, will be demotivated. Meaningful jobs must exemplify the company’s goals and culture.
Individuals, including salespeople, need to be compelled and excited to do their work. It is thus essential to design their jobs with the goal of motivating them. Motivation describes the forces within the individual that account for the level, direction, and persistence of effort expended at work. Appropriate resource allocation allows large organizations to foster and develop innovation in their workforce. Reward systems include compensation, bonuses, raises, job security, and benefits. Job design is the base element for producing effective work organizations, so without meaningful job design, an organization will never operate to its potential.
Designing Territories
Sales territories are the customer groups or geographic districts for which individual sales people or sales teams hold responsibility. Territories can be defined on the basis of geography, sales potential, history, or a combination of factors. Companies strive to balance their territories, because this can reduce costs and increase sales.
Recruiting and Selecting Salespeople
A great deal of recent research has underscored the strategic advantage of managing employees as if they are assets rather than commodities. Making investments in a business’s assets makes a great deal of sense, because these investments will bring a return. A growing number of companies, recognizing that their employees are among their most valuable assets, are backing up that recognition with solid investment.
Recruitment of the Sales Force
Recruitment of talented employees is an essential part of any company’s ability to maintain success and ensure the achievement of standards within an organization. Recruiting sales personnel is no different. Recruiting sales personnel consists of actively compiling a diverse pool of potential candidates which can be considered for employment. In different industries, the constant need for talent creates a highly competitive marketplace for individuals, and it is important for any manager to be aware of these factors as they develop recruitment programs and policies.
Methods of Recruitment: Internal and External
There are two principal ways to recruit workers: internally and externally. Most companies will actively use both methods, ensuring opportunities for existing employees to move up in the organization while at the same time fielding new talent. Internal recruitment is often the most cost effective method of recruiting potential employees, as it uses the existing company resources and talent pool to fill needs.
External recruitment focuses resources on looking outside the organization for potential candidates and expanding the available talent pool. The primary goal of external recruitment is to create diversity among potential candidates by attempting to reach a wider range of individuals unavailable through internal recruitment. Although external recruitment methods can be costly to managers in terms of dollars, the addition of a new perspective within the organization can carry many benefits which outweigh the monetary costs.
Selecting Quality Candidates
After obtaining a large, qualified applicant base, managers need to identify those applicants with the highest potential for success. Selective hiring helps prevent the costly turnover of staff and increases the likeliness of high employee morale and productivity.
To evaluate the fit, it is important for managers to create a list of relevant criteria for each position before beginning the recruitment and selection process. Each job description should be associated with a list of critical skills, behaviors, or attitudes that will make or break job performance. When screening potential employees, managers need to select based on cultural fit and attitude as well as technical skills and competencies. There are some companies, such as Southwest Airlines, based out of the United States, who hire primarily based on attitude because they espouse the philosophy that you hire for attitude, train for skill. According to former CEO Herb Kelleher, “We can change skill levels through training. We can’t change attitude. ” Attitude and personality is especially important for sales positions, as they are often a customer’s first and only point of contact with the company.
Managers must strive to identify the best applicants at the lowest cost. Companies have a variety of processes available to screen potential employees, so managers must determine which system will generate the most accurate results. The methods of selection vary both in levels of effectiveness and in cost of application. In addition to biographical information, companies can conduct personal interviews, perform background checks, and request testing. Because of the costs associated with these measures, companies try to narrow down the number of applicants in each round of hiring.
Sales Training
In general, training provides many diverse benefits both to the company as well as to the salesperson. Training is generally defined as the act of teaching a skill or behavior. However, what does this mean in business terms? Simply put, training in business is the investment of resources in the employees of a company so that they are better equipped to perform the tasks of their job. The type of resources invested may include time to learn, money to create programs and develop training materials, training effectiveness evaluation systems, etc.

Training: Training can be conducted in many ways, such as in a lecture or classroom format (above), online, or any number of ways.
Need for Training
The need for training varies depending on the type of organization that is being discussed; a manufacturing company has different training needs than an insurance firm. But regardless of the type of company being discussed, appropriate training systems can greatly benefit the company. Sales personnel will need different types of specialized training depending on the industry and the company’s unique circumstances.
How does one decide on a training system? The process begins with a training needs assessment. This assessment ought to be a systematic and objective analysis of the training needs in three main areas—organizational, job, and person. Organizational needs deal mostly with the skills the company is looking for, the labor force, etc. whereas the job needs focus on the skills that the company views as necessary for a specific position. Then there are the person needs, and these are the most variable needs. Often these needs arise after a gap is seen in the expected performance compared to the actual performance of the employee. Training can also be a part of a young employee’s “exploration” stage, where training can be used to focus the employee’s interest and development towards a specific area.
Motivating and Compensating Salespeople
Employees are best motivated through effective job design, equitable compensation, and treatment as stakeholders in the company.
Types Of Compensation
Cash is one way to compensate employees, but cash alone is rarely enough payment. Benefits and other forms of non-monetary compensation are becoming more appropriate forms of compensation for employees in today’s workplace. In order to attract, retain, and motivate the best employees, benefits and other sources of non-monetary compensation should be considered. If the company has an understanding of what they can offer to employees, benefits can increase a company’s workforce quality and the general morale of employees.
Companies can offer different types of benefits in order to create a positive culture for their employees. These benefits have the ability to promote social interaction among employees, make life easier for working parents, or improve their quality of life. Depending on the industry and job type, benefits may be more attractive than salary figures. This fact could allow companies to pay lower wages, thus reducing the total amount spent on payroll.
Commission
It is important to design reward systems carefully, taking into consideration base salary and other incentives. This notion applies especially to salespeople. Most compensation systems include “variable pay.” Depending on work performance, many companies reward their employees without affecting the base salary. To reward employees for achieving a set goal, many companies use bonuses. To this point, companies such as GE, HP, and Sun Microsystems use software that directly evaluates the behavior of employees with respect to customer service. Long-term incentives are also a part of reward systems. Stock options and profit-sharing plans are representative of long-term reward systems.
Measuring Sales Force Performance
Appraisals are the common form of measuring how well an employee performed compared to a set of stated objectives; feedback communicates these evaluations.
Performance Appraisals
Historically, performance appraisals have been used by companies for a variety of different purposes, including salary recommendations, promotion and layoff decisions, and training recommendations. In general, “performance elements tell employees what they have to do and standards tell them how well they have to do it” (United States Department of the Interior, 2004). One key item that is often forgotten during the appraisal process (by managers and employees alike) is that the appraisal is for improvement, not blame.
Numerous methods exist for gauging an employee’s performance, and each provides strengths and weaknesses for given environments. Appraisal methodologies depend greatly on the type of work being done; an assembly worker will require a considerably different appraisal system than a business consultant. Similarly, a salesperson will be appraised very differently than a researcher.
Performing an appraisal can be nerve racking for both parties if the situation is not handled correctly. There are many acts a manager can perform to make the process easier on both parties, and hopefully, mutually beneficial. Many assume that performance appraisals are meant to identify weaknesses to be worked on, and exposing these weaknesses can be painful for employees. Studies show that organizations should be leveraging the strengths of each employee rather than focusing on their weaknesses. Yearly performance reviews are becoming increasingly rare as companies begin to see the benefits of frequent appraisal. Constant fine tuning of performance can be much more effective than annual overhauls.
Feedback
In the broadest sense, feedback is simply verbal or nonverbal communication between two or more parties. Feedback should be given in all work situations, good and bad. However, people sometimes think of feedback as being synonymous with criticism when it is given in situations where expectations have not been met. Regardless, we are constantly surrounded by feedback as we see the consequences of our actions and how our actions affect the impressions of those around us, as shown in this feedback diagram.
Figure 10.4.3: Feedback
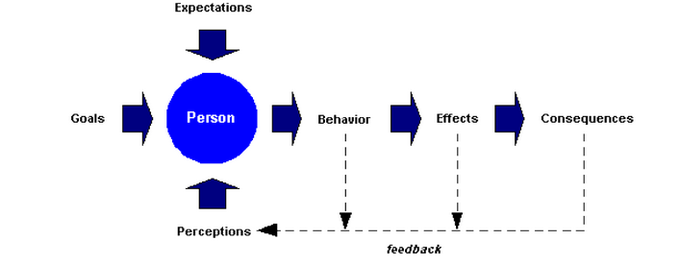
Feedback: Feedback is an essential part of our personal life and our work environment: making, giving, and receiving feedback successfully is critical. This graphic illustrated at feedback impacts perceptions, which impact the individual’s behavior, the effects of that behavior, and the consequences. Each of these aspects can lead to further feedback thus creating a circular effect.
One common problem that managers overlook when reviewing performance is remembering that feedback is not all about forms. Traditional performance reviews have checklists, ratings, or reports that are used as tools to analyze feedback in the organization. While these forms are useful in documenting and appraising a person’s performance, feedback should not be dictated by the type of form an organization uses. Instead, it should be well thought out and measured according to the individual employee in question, considering their unique circumstances and abilities.

