1.1 Matter, mass and volume
Joey Wu and Adam Maltese
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define Matter
- Distinguish between mass and weight
- Calculate the volume of objects with regular or irregular shapes
Matter
Matter is all the “stuff” that exists in the universe. Everything you can see and touch is made of matter, including you! There’s also an enormous amount of matter that you can’t see, but it’s still there – like all the molecules in the air between your eyes and this screen! The only things that are not considered matter are forms of energy, such as light and sound. In science, matter is defined as anything that occupies space and has mass, and it is all around us. Mass and volume measure different aspects of matter.
Mass
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in a substance or an object. The basic SI unit for mass is the kilogram (kg), but smaller masses may be measured in grams (g). To measure mass, you would use a balance to compare its mass with a standard mass.

Figure 1. Balance is usually used to measure the mass of objects.
If both sides of this balance were at the same level, it would mean that the fruit in the left pan has the same mass as the iron object in the right pan. If this was the case, then the fruit would have a mass of 1 kg, the same as the iron. As you can see in Figure 1, however, the fruit is at a higher level than the iron. This means that the fruit has less mass than the iron, that is, the fruit’s mass is less than 1 kg.
Weight versus Mass
Although weight is related to mass, these are not the same thing. Weight refers to the force that gravity exerts on an object. This force is directly proportional to the mass of the object. The weight of an object changes as the force of gravity changes, but its mass does not. An astronaut’s mass does not change just because she goes to space or the moon.

However, her weight on the moon is only one-sixth her earth-bound weight because the moon’s gravity is only one-sixth that of the earth’s. She may feel “weightless” during her trip when she experiences negligible external forces (gravitational or any other), although she is, of course, never “massless.”
Exercise
Check your understanding:
In the following scenario, determine if mass or weight changes
- Alex had a burger as his dinner
- Barbara cut her hair
- Chloe went on a space travel, and landed on the moon for 3 minutes
- Delaney’s dog pooped.
Volume
Volume is a measure of the amount of space that a substance or an object takes up. The basic SI unit for volume is the cubic meter (m3), but smaller volumes may be measured in cm3, and liquids may be measured in liters (L) or milliliters (mL). How the volume of matter is measured depends on its state.
- The volume of a liquid is measured with a special container, such as a measuring cup or graduated cylinder.
- The volume of a gas depends on the volume of its container: gases expand to fill whatever space is available to them.
- The volume of a regularly shaped solid can be calculated from its dimensions. For example, the volume of a rectangular solid is the product of its length, width, and height.
- The volume of an irregularly shaped solid can be measured by the displacement method. An explanation of this method is below.
Calculating Volume from dimensions
Think about the question: how would you find the volume of the metal block in Figure 2?
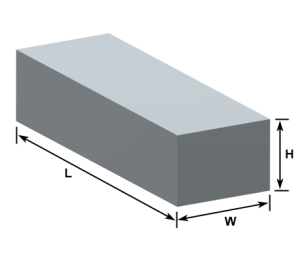
Figure 2. Rectangular metal block
The volume of a rectangular metal block can be calculated with the formula:
Volume = length × width × height
If the length of the block is 50 centimeters, the width is 20 centimeters, and the height is 15 centimeters, then the volume of the metal block is:
Volume = 50 cm × 20 cm × 15 cm = 15,000 cm3
Exercise
How would you find the volume of an object with irregular shape? For example, how would you measure the volume of the Pikachu in Figure 3?

Figure 3. Toy Pikachu
Hint: Search “Displacement Method” to find out.
End of Chapter Practices
- Determine which of the following is matter
- a) a computer
- b) a water bottle
- c) Carbon dioxide
- d) light
- e) orange juice
- f) a balloon full of helium
- What tool do we use to measure the mass of an object?
- What is the SI unit of mass?
- Determine the volume of a rectangular box, with a length of 1 meter, width of 0.7 meters, height of 0.5 meters.
Key Takeaways
- Matter is anythings that occupies a space and has a mass
- Mass measures the amount of matter in a substance or an object. The basic SI unit for mass is the kilogram (kg).
- Volume measures the amount of space that a substance or an object takes up. The basic SI unit for volume is the cubic meter (m3).
Access the content for free via: CK12 Textbook
Media Attributions
- Screenshot 2023-08-08 at 3.53.53 PM
- maejemison_space
- bar-rectangular
- Screenshot 2023-08-08 at 4.23.28 PM

