1.3 Nucleus
Joey Wu
Learning Objectives
- Understand that atoms are the building blocks of matters
- Learn how atoms are constructed.
- Describe basic characteristics of three subatomic particles
Nucleus
If you watched the recent movie Oppenheimer by Christopher Nolan (Summer 2023), you would know that tremendous energy is released from the explosion of an atomic bomb, which is incredibly destructive. Where does all the energy come from? The answer is the nucleus of the atom.
The nucleus (plural, nuclei) is a positively charged region at the center of the atom. It consists of two types of subatomic particles packed tightly together. The particles are protons, which have a positive electric charge, and neutrons, which are neutral in electric charge. Outside of the nucleus, an atom is mostly empty space, with orbiting negative particles called electrons whizzing through it.
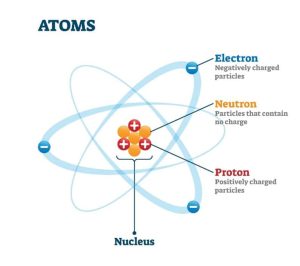
Figure 1. Atomic Structure
Size and Mass of Nucleus
The nucleus of the atom is extremely small. Its radius is only about 1/100,000 of the total radius of the atom. If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a pea!
Electrons have virtually no mass, but protons and neutrons have a lot of mass for their size. As a result, the nucleus has virtually all the mass of an atom. Given its great mass and tiny size, the nucleus is very dense. If an object the size of a penny had the same density as the nucleus of an atom, its mass would be greater than 30 million tons!
To help us better describe atomic mass, scientists introduced the Atomic Mass Unit (AMU). 1 atomic mass unit is equal to the mass of 1 proton or 1 neutron. An atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. A carbon-12 atom has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Therefore, each proton and neutron is approximately 1 AMU. Electrons are much smaller than protons and neutrons, having a mass of approximately
0.0005 AMU, so their effect on the mass of the atom is negligible. Therefore, we usually count the AMU of electrons as zero.
If the nucleus of an atom is the size of a blueberry, how large is the size of this atom?
Key Takeaways
- The nucleus is a small, dense region at the center of the atom. It consists of positive protons and neutral neutrons, so it has an overall positive charge.
- The nucleus is just a tiny part of the atom, but it contains virtually all of the atom’s mass.
Exercises
- Where is most of the mass of an atom located?
-
Sketch a diagram of a boron atom, which has five protons and six neutrons in its nucleus.
-
Sketch a diagram of a helium atom, which has two protons and two neutrons in its nucleus.
Media Attributions
- atom structure

