28 Gustation
Learning Objectives
After reading this section, you should be able to-
- Explain the process by which tastants activate gustatory receptors.
- Trace the path of gustation from gustatory receptors through specific cranial nerves to various parts of the brain.
- Describe the primary taste sensations.
Gustation relies on five primary modalities—salty (Na⁺), sour (H⁺), sweet (sugars & sweeteners), bitter (diverse alkaloids), and umami (L-glutamate)—detected by specialized receptor cells clustered in taste buds on four tongue papillae (circumvallate, foliate, fungiform, filiform). These bipolar gustatory cells release neurotransmitter onto afferent fibers of cranial nerves VII (anterior tongue), IX (posterior two-thirds), or X (extreme posterior), conveying chemical taste information to the brain.
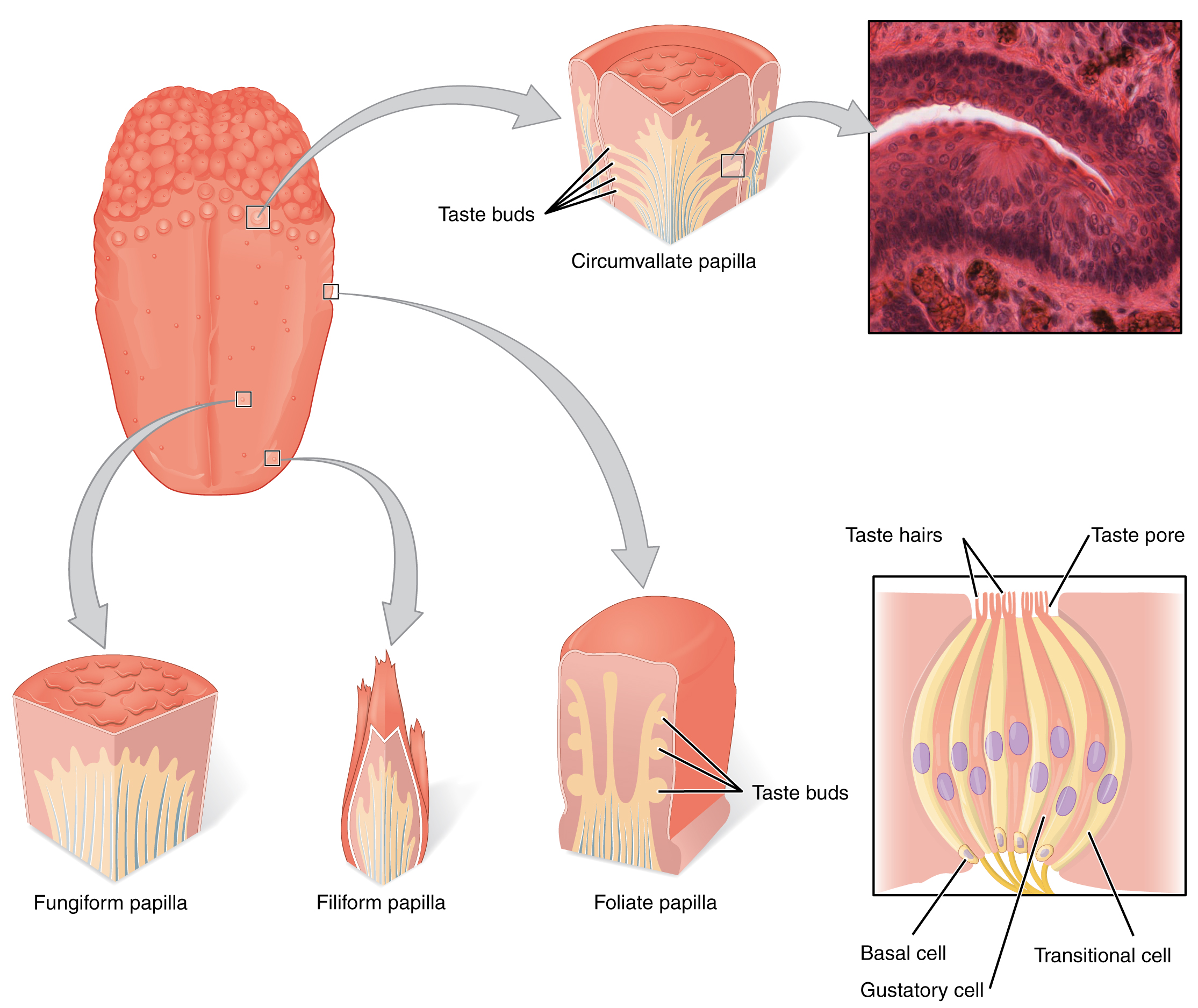
Tasting of Flavors
-
Salty: Na⁺ diffuses through epithelial Na⁺ channels → depolarization → neurotransmitter release
-
Sour: H⁺ enters via proton channels → depolarization → neurotransmitter release
-
GPCR‐Mediated Tastes (Sweet, Bitter, Umami): Tastant binding activates the G-protein gustducin. The Gα subunit of gustducin stimulates phospholipase C-β₂, generating IP₃ and DAG. IP₃ releases Ca²⁺ from intracellular stores, and DAG activates protein kinase C—together amplifying the depolarizing receptor potential → neurotransmitter release
-
Sweet: Glucose and sweeteners bind sweet GPCRs
-
Bitter: Alkaloid and other bitter compounds bind diverse bitter GPCR subtypes (posterior-tongue concentrated for toxin detection)
-
Umami: L-glutamate binds umami GPCRs, signaling savory, protein-rich flavors
-
Central pathway
-
CN VII (facial): anterior 1/3 of tongue
-
CN IX (glossopharyngeal): posterior 2/3 of tongue
-
CN X (vagus): extreme posterior tongue/pharynx
-
→ all converge on solitary nucleus (medulla)
-
→ second-order fibers to ventral posteromedial (VPM) thalamus
-
→ projections to gustatory cortex (insula & frontal operculum)
Central Processing of Taste Information
the sensation of taste
a group of sensory nuclei in the brainstem
the nucleus within the thalamus that relays somato-sensory information

