92 Parturition and postpartum changes
Learning Objectives
After reading this section you should be able to-
-
Define parturition (labor).
-
Explain the hormonal events that initiate and regulate labor.
-
Describe the hormonal regulation of lactation.
Childbirth, or parturition, typically occurs within a week of a woman’s due date, unless the woman is pregnant with more than one fetus, which usually causes her to go into labor early. As a pregnancy progresses into its final weeks, several physiological changes occur in response to hormones that trigger labor.
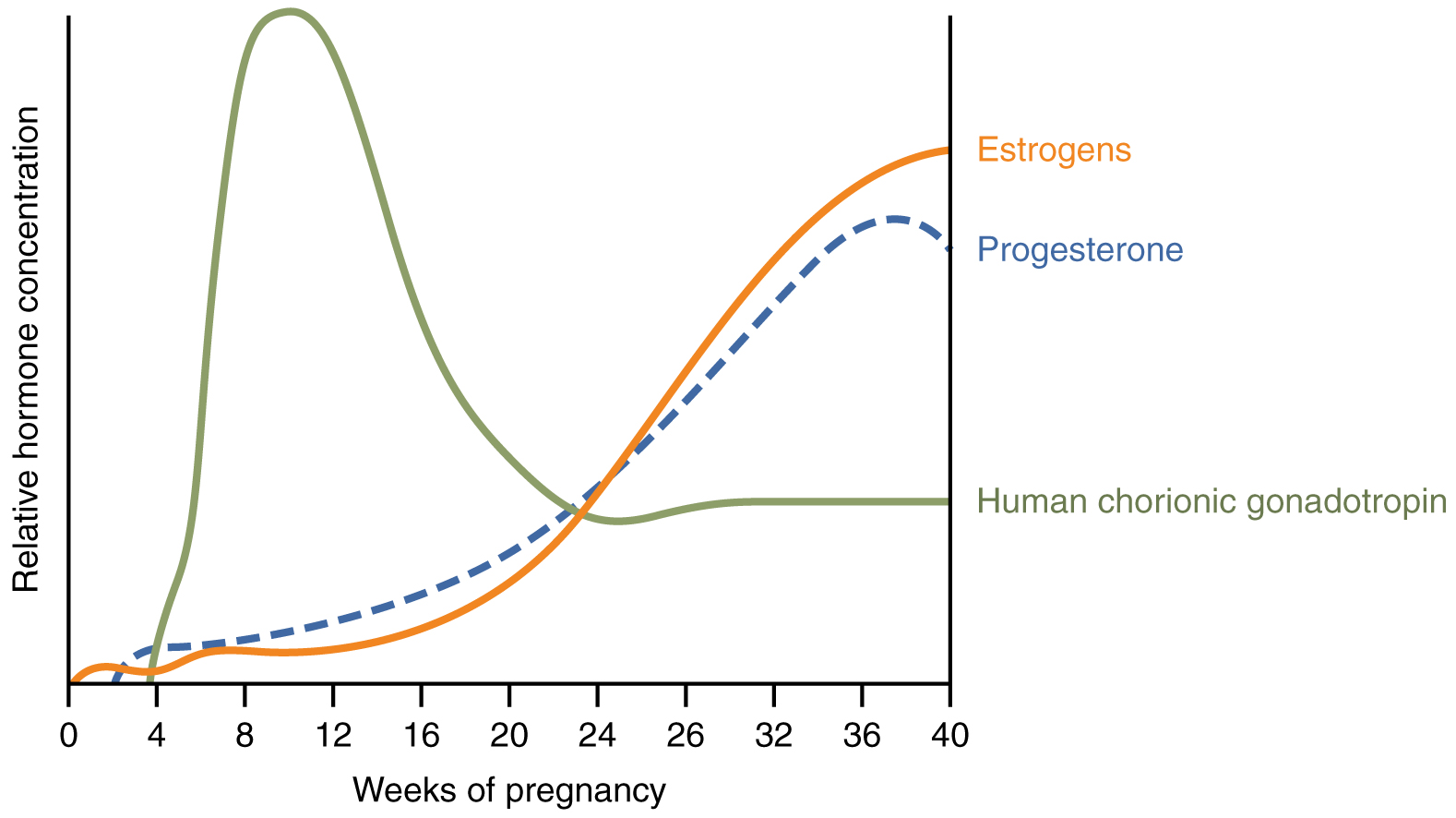
First, recall that progesterone inhibits uterine contractions throughout the first several months of pregnancy. As the pregnancy enters its seventh month, progesterone levels plateau and then drop. Estrogen levels, however, continue to rise in the maternal circulation (Figure 92.1). The increasing ratio of estrogen to progesterone makes the myometrium (the uterine smooth muscle) more sensitive to stimuli that promote contractions (because progesterone no longer inhibits them). Moreover, in the eighth month of pregnancy, fetal cortisol rises, which boosts estrogen secretion by the placenta and further overpowers the uterine-calming effects of progesterone. Some women may feel the result of the decreasing levels of progesterone in late pregnancy as weak and irregular peristaltic Braxton Hicks contractions, also called false labor. These contractions can often be relieved with rest or hydration.
A common sign that labor will be short is the so-called “bloody show.” During pregnancy, a plug of mucus accumulates in the cervical canal, blocking the entrance to the uterus. Approximately 1–2 days prior to the onset of true labor, this plug loosens and is expelled, along with a small amount of blood.
Meanwhile, the posterior pituitary has been boosting its secretion of oxytocin, a hormone that stimulates the contractions of labor. At the same time, the myometrium increases its sensitivity to oxytocin by expressing more receptors for this hormone. As labor nears, oxytocin begins to stimulate stronger, more painful uterine contractions, which—in a positive feedback loop—stimulate the secretion of prostaglandins from fetal membranes. Like oxytocin, prostaglandins also enhance uterine contractile strength. The fetal pituitary also secretes oxytocin, which increases prostaglandins even further. Given the importance of oxytocin and prostaglandins to the initiation and maintenance of labor, it is not surprising that, when a pregnancy is not progressing to labor and needs to be induced, a pharmaceutical version of these compounds (called pitocin) is administered by intravenous drip.
Finally, stretching of the myometrium and cervix by a full-term fetus in the vertex (head-down) position is regarded as a stimulant to uterine contractions. The sum of these changes initiates the regular contractions known as true labor, which become more powerful and more frequent with time. The pain of labor is attributed to myometrial hypoxia during uterine contractions.
Stages of Childbirth
The process of childbirth can be divided into three stages: cervical dilation, expulsion of the newborn, and afterbirth (Figure 92.2).
Cervical Dilation
For vaginal birth to occur, the cervix must dilate fully to 10 cm in diameter—wide enough to deliver the newborn’s head. The dilation stage is the longest stage of labor and typically takes 6–12 hours. However, it varies widely and may take minutes, hours, or days, depending in part on whether the mother has given birth before; in each subsequent labor, this stage tends to be shorter.
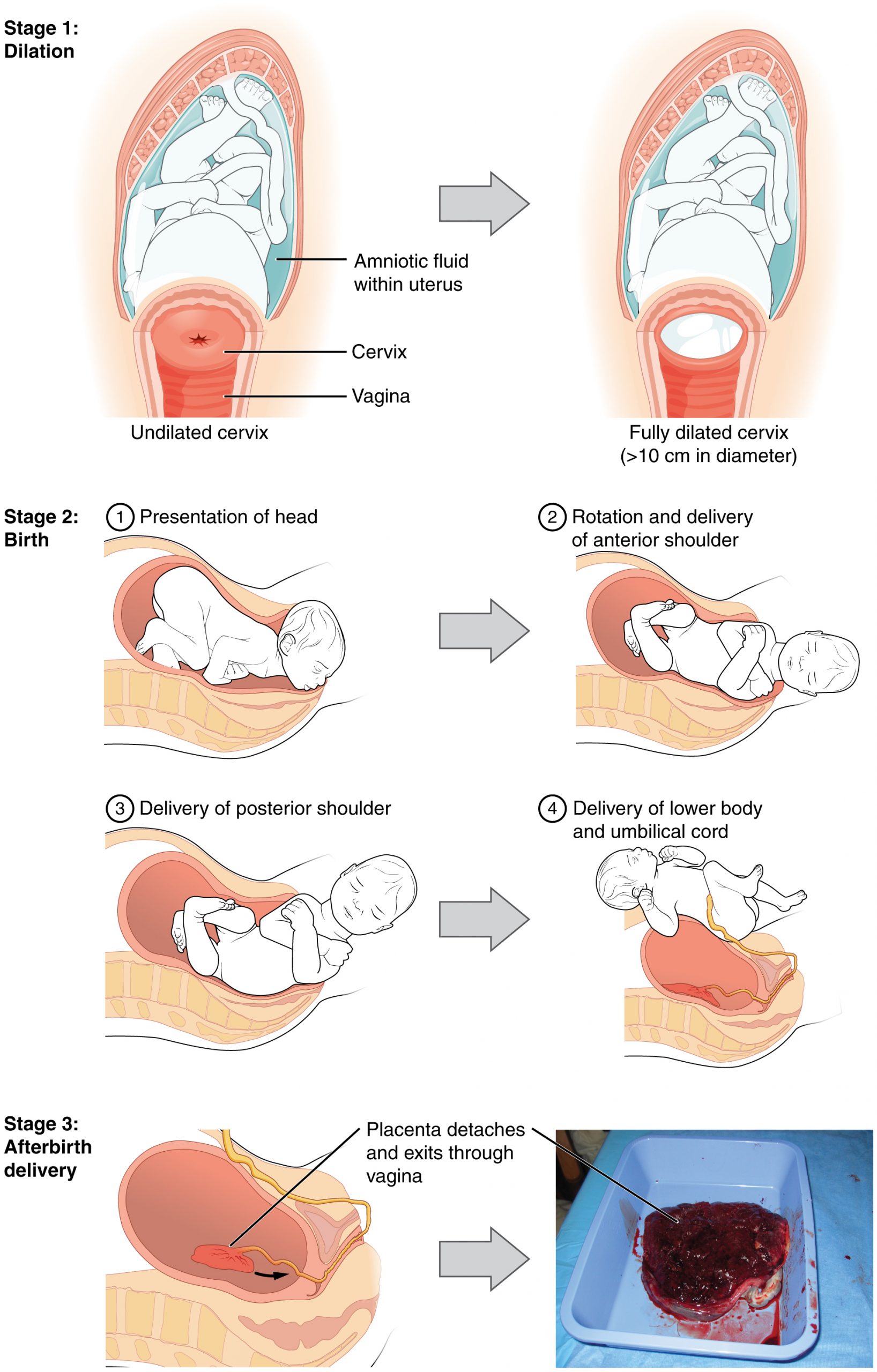
True labor progresses in a positive feedback loop in which uterine contractions stretch the cervix, causing it to dilate and efface, or become thinner. Cervical stretching induces reflexive uterine contractions that dilate and efface the cervix further. In addition, cervical dilation boosts oxytocin secretion from the pituitary, which in turn triggers more powerful uterine contractions. When labor begins, uterine contractions may occur only every 3–30 minutes and last only 20–40 seconds; however, by the end of this stage, contractions may occur as frequently as every 1.5–2 minutes and last for a full minute.
Each contraction sharply reduces oxygenated blood flow to the fetus. For this reason, it is critical that a period of relaxation occur after each contraction. Fetal distress, measured as a sustained decrease or increase in the fetal heart rate, can result from severe contractions that are too powerful or lengthy for oxygenated blood to be restored to the fetus. Such a situation can be cause for an emergency birth with vacuum, forceps, or surgically by Caesarian section.
The amniotic membranes rupture before the onset of labor in about 12 percent of women; they typically rupture at the end of the dilation stage in response to excessive pressure from the fetal head entering the birth canal.
Expulsion Stage
The expulsion stage begins when the fetal head enters the birth canal and ends with birth of the newborn. It typically takes up to 2 hours, but it can last longer or be completed in minutes, depending in part on the orientation of the fetus. The vertex presentation known as the occiput anterior vertex is the most common presentation and is associated with the greatest ease of vaginal birth. The fetus faces the maternal spinal cord and the smallest part of the head (the posterior aspect called the occiput) exits the birth canal first.
In fewer than 5 percent of births, the infant is oriented in the breech presentation, or buttocks down. In a complete breech, both legs are crossed and oriented downward. In a frank breech presentation, the legs are oriented upward. Before the 1960s, it was common for breech presentations to be delivered vaginally. Today, most breech births are accomplished by Caesarian section.
Vaginal birth is associated with significant stretching of the vaginal canal, the cervix, and the perineum. Until recent decades, it was routine procedure for an obstetrician to numb the perineum and perform an episiotomy, an incision in the posterior vaginal wall and perineum. The perineum is now more commonly allowed to tear on its own during birth. Both an episiotomy and a perineal tear need to be sutured shortly after birth to ensure optimal healing. Although suturing the jagged edges of a perineal tear may be more difficult than suturing an episiotomy, tears heal more quickly, are less painful, and are associated with less damage to the muscles around the vagina and rectum.
Upon birth of the newborn’s head, an obstetrician will aspirate mucus from the mouth and nose before the newborn’s first breath. Once the head is birthed, the rest of the body usually follows quickly. The umbilical cord is then double-clamped, and a cut is made between the clamps. This completes the second stage of childbirth.
Afterbirth
The delivery of the placenta and associated membranes, commonly referred to as the afterbirth, marks the final stage of childbirth. After expulsion of the newborn, the myometrium continues to contract. This movement shears the placenta from the back of the uterine wall. It is then easily delivered through the vagina. Continued uterine contractions then reduce blood loss from the site of the placenta. Delivery of the placenta marks the beginning of the postpartum period—the period of approximately 6 weeks immediately following childbirth during which the mother’s body gradually returns to a non-pregnant state. If the placenta does not birth spontaneously within approximately 30 minutes, it is considered retained, and the obstetrician may attempt manual removal. If this is not successful, surgery may be required.
It is important that the obstetrician examines the expelled placenta and fetal membranes to ensure that they are intact. If fragments of the placenta remain in the uterus, they can cause postpartum hemorrhage. Uterine contractions continue for several hours after birth to return the uterus to its pre-pregnancy size in a process called involution, which also allows the mother’s abdominal organs to return to their pre-pregnancy locations. Breastfeeding facilitates this process.
Although postpartum uterine contractions limit blood loss from the detachment of the placenta, the mother does experience a postpartum vaginal discharge called lochia. This is made up of uterine lining cells, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and other debris. Thick, dark, lochia rubra (red lochia) typically continues for 2–3 days, and is replaced by lochia serosa, a thinner, pinkish form that continues until about the tenth postpartum day. After this period, a scant, creamy, or watery discharge called lochia alba (white lochia) may continue for another 1–2 weeks.
Structure of the Lactating Breast
Mammary glands are modified sweat glands. The non-pregnant and non-lactating female breast is composed primarily of adipose and collagenous tissue, with mammary glands making up a very minor proportion of breast volume. The mammary gland is composed of milk-transporting lactiferous ducts, which expand and branch extensively during pregnancy in response to estrogen, growth hormone, cortisol, and prolactin. Moreover, in response to progesterone, clusters of breast alveoli bud from the ducts and expand outward toward the chest wall. Breast alveoli are balloon-like structures lined with milk-secreting cuboidal cells, or lactocytes, that are surrounded by a net of contractile myoepithelial cells. Milk is secreted from the lactocytes, fills the alveoli, and is squeezed into the ducts. Clusters of alveoli that drain to a common duct are called lobules; the lactating female has 12–20 lobules organized radially around the nipple. Milk drains from lactiferous ducts into lactiferous sinuses that meet at 4 to 18 perforations in the nipple, called nipple pores. The small bumps of the areola (the darkened skin around the nipple) are called Montgomery glands. They secrete oil to cleanse the nipple opening and prevent chapping and cracking of the nipple during breastfeeding.
The Process of Lactation
The pituitary hormone prolactin is instrumental in the establishment and maintenance of breast milk supply. It also is important for the mobilization of maternal micronutrients for breast milk.
Near the fifth week of pregnancy, the level of circulating prolactin begins to increase, eventually rising to approximately 10–20 times the pre-pregnancy concentration. We noted earlier that, during pregnancy, prolactin and other hormones prepare the breasts anatomically for the secretion of milk. The level of prolactin plateaus in late pregnancy, at a level high enough to initiate milk production. However, estrogen, progesterone, and other placental hormones inhibit prolactin-mediated milk synthesis during pregnancy. It is not until the placenta is expelled that this inhibition is lifted and milk production commences.
After childbirth, the baseline prolactin level drops sharply, but it is restored for a 1-hour spike during each feeding to stimulate the production of milk for the next feeding. With each prolactin spike, estrogen and progesterone also increase slightly.
When the infant suckles, sensory nerve fibers in the areola trigger a neuroendocrine reflex that results in milk secretion from lactocytes into the alveoli. The posterior pituitary releases oxytocin, which stimulates myoepithelial cells to squeeze milk from the alveoli so it can drain into the lactiferous ducts, collect in the lactiferous sinuses, and discharge through the nipple pores. It takes less than 1 minute from the time when an infant begins suckling (the latent period) until milk is secreted (the let-down). Figure 92.3 summarizes the positive feedback loop of the let-down reflex.
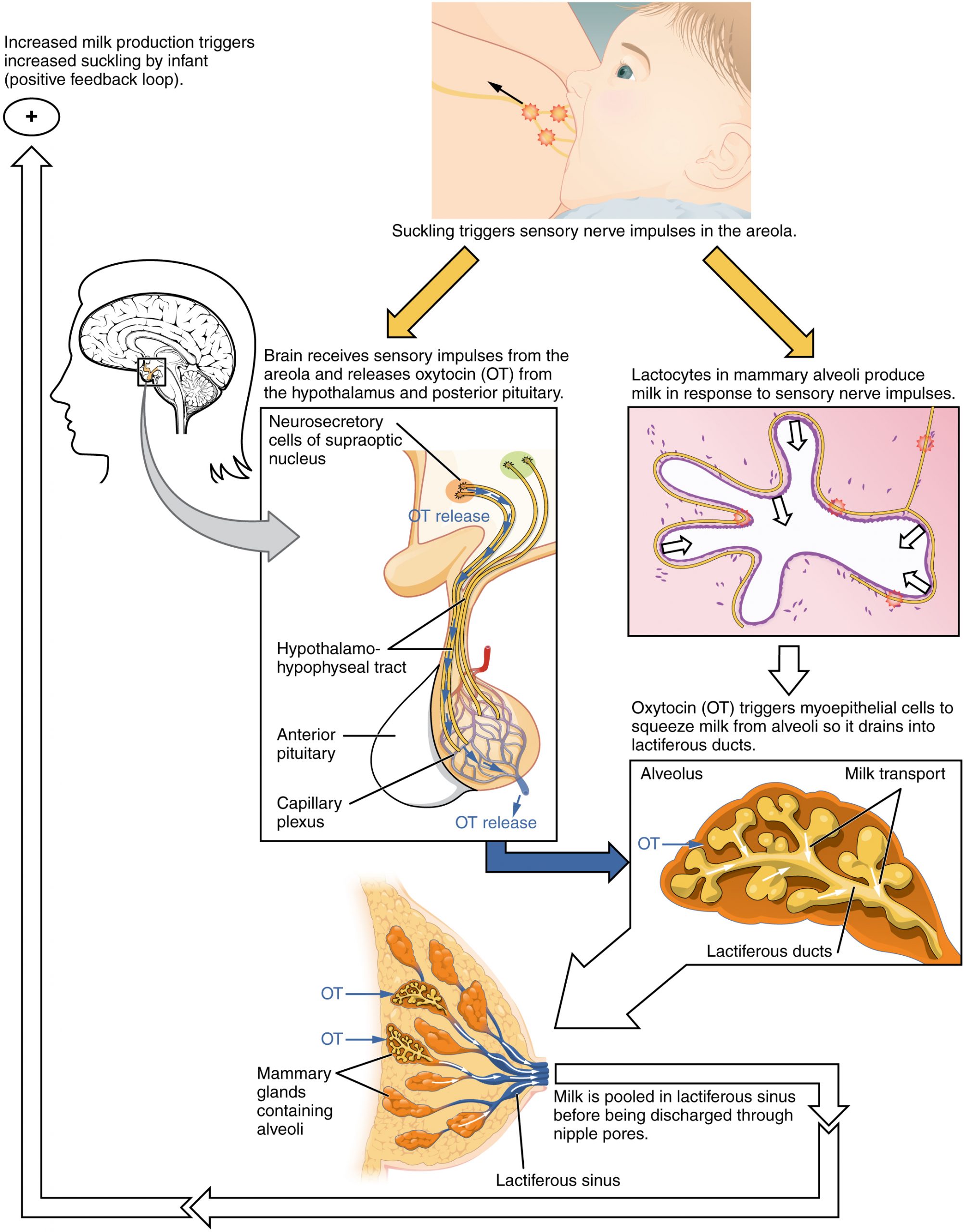
The prolactin-mediated synthesis of milk changes with time. Frequent milk removal by breastfeeding (or pumping) will maintain high circulating prolactin levels for several months. However, even with continued breastfeeding, baseline prolactin will decrease over time to its pre-pregnancy level. In addition to prolactin and oxytocin, growth hormone, cortisol, parathyroid hormone, and insulin contribute to lactation, in part by facilitating the transport of maternal amino acids, fatty acids, glucose, and calcium to breast milk.
Adapted from Anatomy & Physiology by Lindsay M. Biga et al, shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, chapter 28.
childbirth/labour
a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and stored/secreted by the posterior pituitary that induces uterine contractions and milk release from the mammary glands
strong and frequent uterine contractions that cause changes in the cervix, including thinning and dilation
the delivery of the placenta and associated membranes following the delivery of the newborn; the final stage of childbirth
the process in which the uterus shrinks to its original size following all three stages of childbirth
a hormone produced by and secreted from the anterior pituitary that stimulates milk production in the mammary glands of females
automatic positive feedback loop ensuring continuous milk production and let down so long as a baby continues suckling at the breast

