45 Newton-Raphson Method
The Newton-Raphson method allows us to find roots of a nonlinear equation ![]() [9]. That is, this method helps us find
[9]. That is, this method helps us find ![]() such that
such that ![]() .
.
According to this method,
![]()
where ![]() is a root of
is a root of ![]() [9]. The reasoning behind this goes back to the Taylor series. According to Hiestand, we start by developing a Taylor series through the first derivative where
[9]. The reasoning behind this goes back to the Taylor series. According to Hiestand, we start by developing a Taylor series through the first derivative where ![]() and
and ![]() [9]. This give us the following equation.
[9]. This give us the following equation.
![]()
Next, we can suppose that ![]() is a root, as long as a root exists [9]. This implies that
is a root, as long as a root exists [9]. This implies that
![]()
Finally, we solve for ![]() [9].
[9].
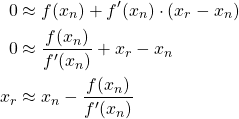
Recall that the closer ![]() is to
is to ![]() , the better the approximation of the Taylor series for
, the better the approximation of the Taylor series for ![]() is. Knowing this, we want to pick
is. Knowing this, we want to pick ![]() such that
such that ![]() is close to the root,
is close to the root, ![]() . Then, substituting
. Then, substituting ![]() into our equation,
into our equation,
![]()
Because ![]() is close to
is close to ![]() , we can then substitute in
, we can then substitute in ![]() to get
to get
![]()
Because ![]() is closer to
is closer to ![]() than
than ![]() is,
is, ![]() is a better approximation for
is a better approximation for ![]() than
than ![]() is. We can then get an even closer approximation by substituting
is. We can then get an even closer approximation by substituting ![]() into the formula, then
into the formula, then ![]() , and so on. With each iteration of this process, we are getting closer to
, and so on. With each iteration of this process, we are getting closer to ![]() .
.
Well, that’s not entirely true. If ![]() is not close enough to the desired root, this process may actually lead us farther away from the root or lead us to another root if more than one exists [9]. Consequently, we need to be careful when choosing
is not close enough to the desired root, this process may actually lead us farther away from the root or lead us to another root if more than one exists [9]. Consequently, we need to be careful when choosing ![]() .
.
Let’s now work through an example that demonstrates the Newton-Raphson method. This problem is one I completed for this paper and comes from Hiebert [9].
Consider the equation
Solution
If ![]() is negative,
is negative, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are all negative. Thus, it is impossible for
are all negative. Thus, it is impossible for ![]() to be negative and a root. So, every root must be greater than or equal to zero. Thus, the smallest root will be the one closest to zero. So, setting
to be negative and a root. So, every root must be greater than or equal to zero. Thus, the smallest root will be the one closest to zero. So, setting ![]() equal to zero seems like a good place to start. We have that
equal to zero seems like a good place to start. We have that
![]()
so the iterations are performed as follows.
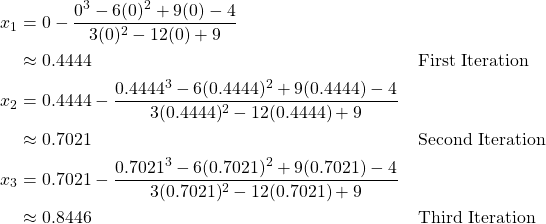
After three iterations, we have
![]()
Because
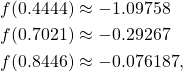
we can see that we are getting closer to a root with each iteration so ![]() was a good choice.
was a good choice.
The Newton-Raphson Method is a great one, but it does have one drawback. We are required to find the derivative. With the example above, it was not difficult to find the first derivative, but not every problem will be that simple. This is the beauty of our next rule, the Secant Rule. It allows us to bypass finding the derivative.
